This article describes how you transfer the content of a “Slackware Live Edition” ISO file onto a USB stick (aka pendrive) thereby making that USB drive bootable, and persistent. The guide is meant for people who are not already running Slackware but still want to try Slackware on a Live USB medium. Note that the parent article “Slackware Live Edition” describes in detail how Slackware users can create such a Live USB drive.
Basically, this divides the article’s audience into:
- Windows users (Windows 7 and higher) with its Boot Configuration Data (BCD) boot record, and
- Linux/BSD users who use GRUB as their boot manager.
I don’t think that LILO is used anywhere else than in Slackware. LILO does not support ISO images as boot selection, but it is still possible to make LILO boot Slackware Live. If you are not using Slackware but your OS is actually using LILO, let me know in the comments section and I will update this article with guidelines.
Why another guide if there’s a lot of documentation already?
It’s easy to use ‘dd’ or an equivalent Windows tool to copy the ISO file onto a USB stick, but then you end up with a read-only stick. The ISO9660 filesystem which is used for generating the ISO file, is read-only by nature and the ‘dd’ command copies everything, re-creating a read-only filesystem on the target.
People who want a Live USB stick with persistence, need to run the accompanying “iso2usb.sh” script which does some smart thngs to the USB stick to make it writable for the Live OS. However, using that script outside of Slackware seems to be an issue for some people.
Therefore this guide will show you how to:
- boot your computer to Slackware Live directly from a downloaded ISO.
- Subsequently write the ISO’s contents to your USB stick from within Slackware Live Edition. How? Because the “iso2usb.sh” script is contained inside that ISO and will be available to you in the Live OS.
Step 1: adding Slackware Live Edition to your computer’s boot menu
Windows 7 and newer:
Download and install EasyBCD from Neosmart Technologies. This software is free for non-commercial use. EasyBCD will allow you to add a Linux OS partition to the Windows bootmenu (that is what I use it for on computers that need to keep the Windows bootloader instead of switching to LILO or GRUB). It is much more versatile than that: for our current purpose, it is also able to make the computer boot from an ISO image stored on the local harddisk.
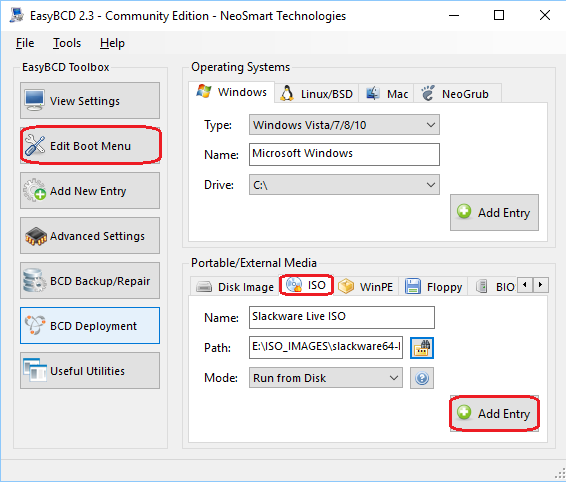
Start EasyBCD (it will ask for permission to run as an administrator) and add a new boot menu entry for the Slackware Live ISO:
- Click the “Add New Entry” button.
- In the “Portable/External Media” area click the “ISO” tab.
- Write the name you want to see in the boot menu, in the “Name” text entry field. For instance “Slackware Live ISO”.
- Leave the “Mode” to the default ‘Run from Disk‘ unless you want to wait a long time for the ISO to load into the computer’s RAM before booting (in which case you can select ‘Load from Memory‘).
- In the “Path” entry field you should select the full path to the ISO file of the Slackware Live Edition which you downloaded to your local hard drive.
- Click the “Add Entry” button.
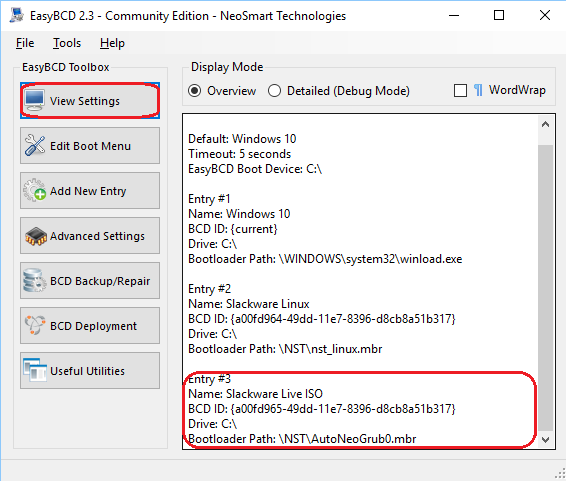
The “View Settings” will now show your new boot entry. You will notice that a new directory was created in the root of the Windows boot drvive (usually that is the C drive), called ‘NST’, which contains a single-purpose master boot record to boot the ISO image:
After rebooting your Windows computer you will see the new option “Slackware Live ISO” in the Windows Boot Manager screen. Select that option and watch your computer boot into Slackware Live. There are some remaining items to take care of before you can login:
- Don’t let the OS boot into the default settings. You have 30 seconds to do the following: in the syslinux or grub boot menu, you need to edit the boot commandline (in syslinux you need to press “TAB” and in grub you need to press “e” to edit the commandline).
- To the existing boot command parameters you have to add one more: “livemedia=/dev/sdX1:/path/to/slackware64-live-current.iso” or else liveslak will not be able to find its own media…
You need to change “/path/to/slackware64-live-current.iso” to the actual full path and filename of the ISO you downloaded. Use Linux forward slashes “/” to separate the directories even though the filesystem is probably NTFS where you would want to use Windows backslashes “\” instead.
The “/dev/sdX1” is your harddisk’s root partition.- Instead of the devicename of the partition (/dev/sdX1), you can also write the UUID or the Label of the partition’s filesystem.
- If the partition containing the ISO file is not the first partition on the disk, you need to adjust the device numbering in the above example (the orange “1” occurrences).
- If you know the filesystem path to the ISO but you do not know how your Windows partition translates to a Linux devicename, you can boot the ISO without the “livemedia” boot parameter but instead use the extra parameter “debug=4“. Then let the ISO boot – it will deliver you into a “debug shell” where you can use a command like “fdisk -l” or “gdisk -l /dev/sda” to inspect the partition layout of your harddisk(s). When you are ready, press the computer’s “RESET” button to reboot and try again.
- In liveslak 1.1.9 and newer, you will not have to worry about the ‘/dev/sdXX’ partition name and you can specify “scandev” instead. The syntax “livemedia=scandev:/path/to/isoimagefile” has been implemented to let liveslak search for the partition itself – you still have to specify the full path to the Live ISO file though.
GRUB version 2 and higher
I do not know about Grub 1.x (Grub Legacy)… probably no one uses this version anymore, but at least GRUB2 is able to loop-mount an ISO file and then access the kernel plus initrd inside the ISO image – and boot from these.
Pre-requisite is that you downloaded the Slackware Live ISO to your local harddisk – let’s assume that it is located in /home/alien/slackware64-live-current.iso .
- Open the grub local customization file in an ASCII editor (as root!): “/etc/grub.d/40_custom”. We will add our custom entry here, and afterwards we run “grub-update” to update the GRUB2 bootmenu.
- To the bottom of that file, add these lines (mind the backslashes – you should remove them, they are only added for better readability on this blog page):
menuentry “Slackware Live ISO” { set isofile=”/home/alien/slackware64-live-current.iso” loopback loop (hd0,1)${isofile} linux (loop)/boot/generic livemedia=scandev:${isofile} \ load_ramdisk=1 prompt_ramdisk=0 rw printk.time=0 \ kbd=us tz=localtime locale=us_EN.utf8 initrd (loop)/boot/initrd.img }
…where “/dev/sdX1” is the Linux naming convention and “(hd0,1)” the grub naming convention for your harddisk’s root partition.
In liveslak 1.1.9 and newer, you will not have to worry about the ‘/dev/sdXX’ partition name, because the syntax “livemedia=scandev:${isofile}” has been implemented to let liveslak search for the partition itself. - In case you are stuck with a pre-1.1.9 release of liveslak and can not use “scandev”, then instead of the devicename of the partition (/dev/sdX1), you can also use the ‘UUID’ or the ‘Label’ of the partition’s filesystem.
If the partition containing the ISO file is not the first partition on the disk, you need to adjust the device numbering in the above example (the orange “1” occurrences).
If you know the filesystem path to the ISO but you do not know how your Windows partition translates to a Linux devicename, you can boot the ISO without the “livemedia” boot parameter but instead use the extra parameter “debug=4”. Then let the ISO boot – it will deliver you into a “debug shell” where you can use a command like “fdisk -l” or “gdisk -l /dev/sda” to inspect the partition layout of your harddisk(s). When you are ready press the computer’s “RESET” button to reboot and try again.
NOTE:
In the “menuentry” example above I have used backslashes ( \ ) to split a long line (the one starting with “linux”) into 3 lines. This was done for readability! When you copy the above example into your “/etc/grub.d/40_custom” file, you must remove the two backslashes ( \ ) and join the three broken-up lines back into one single line that starts with “linux” and ends with “utf8“. - Run “update-grub” to re-generate the Grub master configuration.
If you get a “update-grub: command not found” error, that is easily fixed. In some distro’s the “update-grub” script was added, and some others like Slackware do not have it. The content of that “update-grub” script is:#!/bin/sh set -e exec grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg "$@"You can easily create a new file “/sbin/update-grub” as root, copy the above lines into it, and after saving this file you run “chmod +x /sbin/update-grub” to make the script executable.
Note that there may be distributions that rename “grub-mkconfig” to “grub2-mkconfig”. In that case, adjust the contents of your new “update-grub” script accordingly.
After rebooting your Linux computer you will see “Slackware Live ISO” as a new selectable option in your GRUB boot menu. Select that, and watch your computer boot into Slackware Live Edition.
Step 2: transferring the content of the ISO to your USB stick
This is the easy part, as it has been documented extensively in earlier blog articles. Also see the official documentation on Slack Docs for this transferal process. I will repeat it here for completeness’ sake:
After completing Step 1 from this guide, you are now running Slackware Live Edition on your computer, booted straight from the ISO file which is located somewhere on the computer’s harddisk.
Let’s login and mount that harddisk partition’s filesystem into the Live OS:
- Login to the graphical session manager which you see on screen. Use the account “live” with the password “live”.
- You will end up in a graphical desktop session (KDE, XFCE, MATE, PLASMA5 depending on the ISO variant you downloaded. Start a terminal emulator like “konsole” in KDE or a more basic choice like “xterm”. Any terminal will do.
- In the terminal, switch user to become root. The password you need to type for the ‘su’ (and also for ‘sudo’) command is again “live”:
$ su -
- Now that you are root, mount the harddisk partition to the Live OS directory “/mnt/hd” so you can access the ISO file there later:
# mount /dev/sdX1 /mnt/hdLike with Step 1, you must substitute the example “/dev/sdX1” with the actual partition name on the harddisk, to where you downloaded the ISO. Use the command ‘fdisk -l’ to see what partitions are available if you are unsure about which one you need.
- Plug in your USB stick. Make sure it does not get mounted. If it gets mounted automatically, you need to un-mount it again, manually.
- A script is available which allows you to transfer the ISO content to a USB stick, making some modifications depending on the script’s parameters. The USB stick will be erased and re-formatted when running this script! Before inflicting any irreversible damage, the script will show you a prompt at which point you can evaluate whether it is safe to continue.
This script, called ‘iso2usb.sh‘, accepts the following parameters:
-c|--crypt size|% Add a LUKS encrypted /home ; the parameter
is the requested size of the container in
kB, MB, GB,or as percentage of free space.
Examples: '-c 125M', '-c 1.3G', '-c 20%'.
-f|--force Ignore most warnings (except the back-out).
-h|--help This help.
-i|--infile Full path to the ISO image file.
-o|--outdev The device name of your USB drive.
-p|--persistence Custom name of the 'persistence' directory/file.
-r|--refresh Refresh the USB stick with the ISO content.
No formatting, do not touch user content.
-u|--unattended Do not ask any questions.
-v|--verbose Show verbose messages.
-w|--wait Add X seconds wait time to initialize USB.
-C|--cryptpers size|% Use a LUKS-encrypted 'persistence' file instead
of a directory (for use on FAT filesystem).
-P|--persistfile Use an unencrypted 'persistence' file instead
of a directory (for use on FAT filesystem).
Examples:
Note1 -the “#” at the beginning of these examples is an indication that you need to run the command as root. The “#” is not part of the command!
Note2 – the value for the output parameter is the device name of the stick and not one of its partitions!
- Create a USB version of Slackware Live, where the USB stick is known to the system as ‘/dev/sdX.
# iso2usb.sh -i /mnt/hd/home/alien/slackware64-live-current.iso -o /dev/sdX - Create a USB Live like above, but this time adding an encrypted /home filesystem with 750 MB of space, and at the same time increase the wait time on boot to 15 seconds (useful for slow USB media that fail to start the Live OS otherwise):
# iso2usb.sh -i /mnt/hd/home/alien/slackware64-live-current.iso -o /dev/sdX -c 750M -w 15 - Create a USB Live with an encrypted /home (allocating 30% of the stick’s free space for /home) and where the persistent data will be stored in a container file instead of a directory:
# iso2usb.sh -i /mnt/hd/home/alien/slackware64-live-current.iso -o /dev/sdX -c 30% -P - Create a USB Live with both the /home and the persistent data encrypted (the persistence filesystem will be 300 MB in size):
# iso2usb.sh -i /mnt/hd/home/alien/slackware64-live-current.iso -o /dev/sdX -c 30% -C 300M
You might have noticed that the “-P” parameter does not accept a size parameter. This is because the un-encrypted container file is created as a ‘sparse’ file that starts at zero size and is allowed to grow dynamically to a maximum of 90% of the initial free space on the Linux partition of the USB stick.
Good luck! Eric
PS: if you took the time to scroll all the way down, and if you would rather want to use the “iso2usb.sh” on your non-Slackware distro instead of going through all the hassle of this guide, please give me feedback about the errors and issues you find when running the script in your distro.
I absolutely wish that the script works perfectly on any distro, not just Slackware. If you have suggestions or patches, those are very welcome!
 Slackware turned 24 today, 17 July.
Slackware turned 24 today, 17 July.

Recent comments