Hi all!
 Welcome to the fourth episode in a series of articles that I am writing about using Slackware as your private/personal ‘cloud server’.
Welcome to the fourth episode in a series of articles that I am writing about using Slackware as your private/personal ‘cloud server’.
Check out the list below which shows past, present and future episodes in the series, if the article has already been written you’ll be able to click on the subject.
The first episode also contains an introduction with some more detail about what you can expect.
These articles are living documents, i.e. based on readers’ feedback I may add, update or modify their content.
Nextcloud Productivity Platform
So far, I have explored Docker container infrastructure management, shown you how to build an Identity and Access Management service in Docker and used that to make a Video Conferencing platform available to the users of your Slackware Cloud server. Today we are going to explore other means of collaboration and personal productivity.
Some of the topics in the current Episode will cover cloud storage: how do you share your data (documents, music, photos, videos) across your computers with a safe backup copy on your Cloud server? How do you keep track of your activities, read your emails, plan your work, chat with your friends and setup video calls with them? Moreover, how can I achieve all of this without having to depend on the Cloud plaforms that Google, Dropbox, Amazon, Microsoft offer and which seem free but are most certainly not?
The Nextcloud platform which is the main topic of this article, offers a solution to this dilemma. Nextcloud is a spin-off from ownCloud. It was announced in 2016 by the original founder of ownCloud after he left the company because he did not agree to the course ownCloud was going to take. OwnCloud now offers part of its features exclusively as a paid-for subscription model, whereas Nextcloud is fully open source and all features are available to community users as well as paying customers.
The core of Nextcloud is called the Nextcloud Hub, the server product which integrates the three main components Files, Talk and Groupware and which you can host and manage on a server which you own and control. Client programs are available for Linux, Windows and Android platforms that allow you to sync your local files to the server, participate in videoconferences directly from your phone etc.
The goal of setting up Nextcloud on our Slackware Cloud Server is to achieve total control over your data, share these data securely with other people and eliminate dependencies on similar commercial offerings while enjoying the same functionality.
But first a slight detour before we dive into the setup of our Collaboration Platform.
Nextcloud allows for document collaboration in similar fashion to Microsoft Office 365. This is a topic which has its own Episode in the article series: the next one called “Collaborative Document Editing” will center around the integration of Collabora Online Development Edition (CODE) into our Nextcloud Hub.
Collabora is a major contributor to the LibreOffice suite. An online web-based front end to LibreOffice programs was initiated and is being developed by Collabora since 2014, and in essence, Collabora Online is the continued development of the original ‘LibreOffice Online’ code. Collabora moved the repository to github and it is the source used to build CODE, but is also used to create an “enterprise” version which has a paid subscription model. The pre-compiled CODE binaries have a limitation of 10 simultaneously edited documents, but compiling the source yourself will circumvent this artificial limitation.
Preamble
For the scope of this article I will assume that you have a Slackware 15.0 server with IP address “10.10.10.10“. Your own IP address is of course different but your (web)server needs to be accessible online.
Our example server (you need to apply real-life values here of course) has the following configuration:
- a working Docker environment;
- Apache httpd configured and running and reachable as “
https://darkstar.lan/” with the DocumentRoot directory “/var/www/htdocs/” which is the default location for Apache httpd’s content in Slackware.
- Keycloak configured and running at “https://sso.darkstar.lan/auth/”;
- Jitsi Meet configured to use Keycloak for authentication and running at “
https://meet.darkstar.lan/“; with the keycloak-jitsi bridge at “https://sso.meet.darkstar.lan/“.
- PHP version 7.3, 7.4 or 8.0, which is the reason for the Slackware 15.0 requirement – the PHP of Slackware 14.2 is just too old.
Nextcloud Hub II
The Nextcloud Hub II is the new name of the Nextcloud server product which you can download as a single ZIP file and install into your webserver. Nextcloud Hub can be extended with plugins and for that, there is an active App Store. The Nextcloud administrator can search for, install, enable, disable, update, configure and remove these applications from the web-based management console or even from the command-line. This article will discuss some of these applications, in particular the ‘featured apps‘ which are the ones that are supported or developed by Nextcloud GmbH directly.
The core of Nextcloud Hub II consists of the following components:
Files:
Nextcloud Files allows easy access to your files, photos and documents. You can share files with other Nextcloud users, even with remote Nextcloud server instances. When CODE is installed (see the next Episode in this Series) you can even collaborate on documents in real-time with friends, family, team members, customers etc. We have inherent security through data encryption (in transit and on the local file storage) and access control mechanisms, so that only those people with whom you explicitly share your file(s) will be able to access them.
Users store files in their account and this translates to a per-user directory in the host’s filesystem. By default this storage area is not encrypted. If you don’t feel at ease with the idea that unauthorized access to the server potentially exposes userdata to the intruder, the Nextcloud administrator can enable on-disk encryption of all the users’ files. Once encrypted, the userdata can not be decrypted by anyone else than the owner of the files (aka the user) and those with whom files are shared. An encryption key is created per user and the user’s password unlocks that key which is always and only stored on the server. If the user loses their password, they will permanently lose access to their data!
The administrator can configure a ‘recovery key‘ however. You may pose that this allows that administrator to gain access to the userdata, but that’s the other side of the coin of being able to decrypt userdata in the event of loss of the password…
Talk:
Nextcloud Talk offers screensharing, online meetings and web conferencing. The video conferencing capabilities are not yet as strong as Jitsi Meet (in particular it does not scale well to a lot of simultaneous users) but the Talk component is being improved continuously.
Groupware:
Nextcloud Groupware consists of easy to use applications for Webmail, Calendaring and Contacts and is integrated with Nextcloud Files. In webmail you can configure multiple IMAP server accounts, PGP encryption is supported. Calendars can be shared and have Nextcloud Talk integration for video conferences. You can create appointments and define and book resources. Contacts can be grouped, shared with others, and synchronized to and from your phone.
In addition, you can install the featured app ‘Deck‘ which enables you to manage your work with others through private or shared Kanban-style task boards.
Setting up MariaDB SQL server
Nextcloud Hub uses a MariaDB server as its configuration back-end. The users’ files are stored in your host file-system.
You could use SQLite instead… but that is really going to affect the performance of your server negatively if the load increases. In case you have never setup a MariaDB SQL server, I will give you a brief rundown.
MariaDB is part of a full installation of Slackware, and since ‘full install‘ is the recommended install, I will assume you have a mariadb package installed. If not, because you decided to do only a partial installation on your server, be sure to start with an installation of mariadb and its dependencies lz4 and liburing.
- Create the system tables for the SQL server:
# mysql_install_db --user=mysql
Installing MariaDB/MySQL system tables in '/var/lib/mysql' ...
OK
- Make the MariaDB boot script executable:
# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.mysqld
- Comment the ‘
SKIP="--skip-networking" ‘ line in ‘rc.mysqld‘ because we will use client connections from outside.
- Execute the boot script (or reboot the machine):
# /etc/rc.d/rc.mysqld start
- Perform initial configuration of the database server:
# /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] n
Set root password? [Y/n] y
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
This script locks down your SQL server properly. It will prompt you to setup the admin (root) password and gives you the option of removing the test databases and anonymous user which are created by default. This is strongly recommended for production servers. I answered “NO” to “Switch to unix_socket authentication” because the Docker containers on our Slackware Cloud server will need to access this MariaDB SQL server over the local network.
You now have MariaDB SQL server up and running, the root (admin) password is set and the root user can only connect to the database from the localhost. It’s ready to setup its first database.
We will manually create the required SQL database for NextCloud (you might want to insert your own account/password combo instead of my example “nextcloud/YourSecretPassword“). Since we are installing NextCloud on the ‘bare metal‘, NextCloud can communicate with the SQL server via the ‘localhost‘ network address:
# mysql -uroot -p
> CREATE USER 'nextcloud'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'YourSecretPassword';
> CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS ncslack CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci;
> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ncslack.* TO 'nextcloud'@'localhost';
> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
> quit;
Configuring Apache and PHP
First of all, we are going to increase the PHP memory limit from the default 128 MB to 512 MB (recommended value) in the file ‘/etc/php.ini‘ or else the more complex operations will fail:
memory_limit = 512M
Don’t forget to enable PHP support in “/etc/httpd/httpd.conf” by un-commenting the line:
‘Include /etc/httpd/mod_php.conf‘.
Your Apache server needs some directives inside the ‘<VirtualHost></VirtualHost>‘ block that are not enabled by default.
This section needs to be added:
<Directory /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/>
Require all granted
Satisfy Any
AllowOverride All
Options FollowSymLinks MultiViews
<IfModule mod_dav.c>
Dav off
</IfModule>
</Directory>
Alias "/localapps" "/opt/netxtcloud/localapps"
<Directory "/opt/nextcloud/localapps">
Require all granted
AllowOverride All
Options FollowSymLinks MultiViews
</Directory>
Also, the Apache httpd modules mod_rewrite, mod_headers, mod_env, mod_dir and mod_mime need to be enabled. This is usually done in ‘/etc/http/httpd.conf‘.
Configuring local storage
We are going to maintain all of the Nextcloud users’ personal data separately from the server code and even outside of the webserver document root. Nobody should be able to access your files through a possible hole in your webserver.
Also, when the Nextcloud administrator (you) is going to extend the server’s functionality by installing additional apps, you will want these apps to be installed outside of the Nextcloud application directory. This allows for a clean upgrade process if we want to install a newer version in the future. The “/opt/nextcloud/” will be the root directory for all of this. The httpd user account “apache” needs to own these files.
Let’s start with creating the userdata directory:
# mkdir -p /opt/nextcloud/data
# chown apache:wheel /opt/nextcloud/data
And the directory where the add-ons will be installed:
# mkdir -p /opt/nextcloud/localapps
# chown apache:wheel /opt/nextcloud/localapps
To the Apache httpd VirtualHost configuration you should add an ‘Alias‘ statement which points the webserver “/localapps” path component to the filesystem location “/opt/nextcloud/localapps“. This line was already mentioned in the Apache configuration snippet further up:
Alias "/localapps" "/opt/netxtcloud/localapps"
Installing the Nextcloud Hub
We will download the latest stable release from their server installation page.
At the time of writing, 23.0.0 is the latest available so:
# cd ~
# wget https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/nextcloud-23.0.0.zip
# unzip -n nextcloud-23.0.0.zip -d /var/www/htdocs/
# chown -R apache:wheel /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/
We have already created the SQL database, so we can immediately continue with the Web setup. Point your browser at http://darkstar.lan/nextcloud/ :
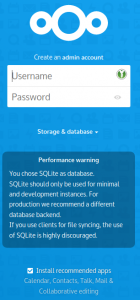
This is where you will define the account and password for the Nextcloud administrator. It will be the only account with local credentials (stored in the SQL backend). All future Nextcloud user authentication & authorization will be configured and managed via the Keycloak IAM program. The green text snippets match with configuration settings documented higher up in this article.
- I will use the name “
admin” for the account and give it a secure password.
- Storage & Database:
- Data Folder: “/opt/nextcloud/data“
- Database: MySQL/MariaDB
- Database user: “nextcloud“
- Database password: “YourSecretPassword“
- Database name: “ncslack“
- Localhost: add the MariaDB port number so that it reads “localhost:3306”
- Install recommended apps: Calendar, Contacts, Talk, Mail & Collaborative editing: ensure that this box is checked (note that the Collaborative Editing program – CODE – download will probably fail but we will install it as an external application later):
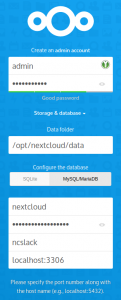
TIP: I experienced that when the password fields are set to “show password”, the installation will refuse to continue.
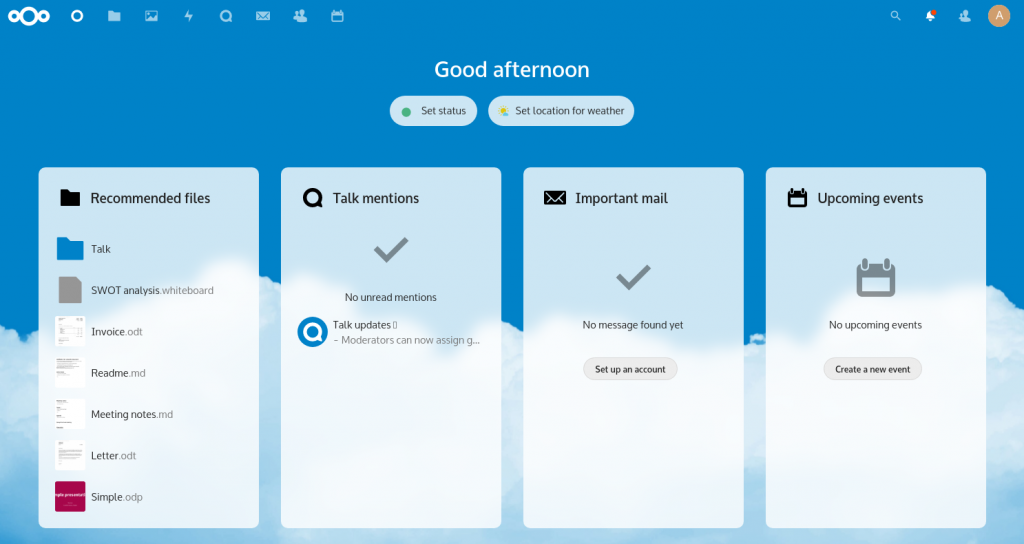
Click “Finish” to kick off the Nextcloud setup.

This configuration process ends with some screens that will show off the capabilities of the programs, you can either close these immediately (the “X” top right) or click through them until the end. You will end up in your Nextcloud dashboard:
Post-configuration
After installation and initial configuration we are now going to tune the server.
Pretty URLs
A Nextcloud URL looks like “http://localhost/nextcloud/index.php/apps/dashboard/” and I want to remove the “index.php” string which makes the URLs look nicer. Check the official documentation.
- Edit “
./config/config.php” file in the nextcloud directory. Add the following two variables right before the last line which goes like “);“:
‘overwrite.cli.url’ => ‘https://darkstar.lan/nextcloud’,
‘htaccess.RewriteBase’ => ‘/nextcloud‘,
- We are going to use the NextCloud command-line interface ‘
occ‘ (here it shows its heritage; ‘occ‘ stands for ‘Own Cloud Console‘) in order to apply the changes in ‘config.php‘ to the ‘.htaccess‘ file in the NextCloud installation directory.
The ‘occ’ command needs to be run as the httpd user (‘apache‘ in the case of Slackware):
# sudo -u apache php -d memory_limit=512M /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/occ \
maintenance:update:htaccess
.htaccess has been updated
Note that I have not been able to get this to actually work! Pointers with a fix for pretty URLs are welcome!
Server scan
You can run a “server scan” as admin user via “Settings > Administration > Security & Setup Warnings” to see if Nextcloud has suggestions on improving performance and functionality of the server.
In my case, it reports that a number of database indexes are missing, and that the following commando will fix this:
# sudo -u apache php /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/occ db:add-missing-indices
This scan will also point out performance issues about which I will share more details, below in “Tuning server performance” section.
Cron maintenance
It is advised to install a cron job which runs as the “apache” user, and performs maintenance every 5 minutes. In Nextcloud as the admin user, you configure the “Cron” maintenance type via “Settings > Administration > Basic Settings > Background Jobs“.
This needs to be accompanied by an actual cron job definition on the Slackware server; so this is the command that I added to the crontab for “apache“:
# crontab -u apache -l
# Run maintenance for NextCloud every 5 minutes:
*/5 * * * * /usr/bin/php -f /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/cron.php
Install add-on applications outside of Nextcloud directory
We have already created a ‘/opt/nextcloud/localapps‘ directory with the intention of using that location for the installation of all the apps that we want to add to our Hub.
In order to enable a separate application installation path, you need to add the following lines to ‘./config/config.php‘:
'appstoreenabled' => true,
'apps_paths' => array(
array(
'path'=> OC::$SERVERROOT . '/apps',
'url' => '/apps',
'writable' => false,
),
array(
'path'=> '/opt/nextcloud/localapps',
'url' => '/localapps',
'writable' => true,
),
),
Note that if you get an error from external applications when they attempt to parse the ‘config.php’ file of NextCloud which looks like “Expected boolean literal, integer literal, float literal, string literal, ‘null’, ‘array’ or ‘[‘”, you may have to replace:
'path'=> OC::$SERVERROOT . '/apps',
with
'path'=> '/var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/apps',
Tuning server performance
Memory cache
The main optimizations which will boost your server’s performance and responsiveness are related to memory caching and transactional file locking.
You can address these both by installing redis (an in-memory key-value memory store) and php-redis (PHP extension for redis) as Slackware packages from my repository:
After installing redis, configure it correctly for Nextcloud.
- Enable the php redis extension by editing ‘
/etc/php.d/redis.ini‘ and removing the semicolon so that you get the following line:
; Enable redis extension module
extension=redis.so
Optionally add these lines to tune its performance:
; Should the locking be enabled? Defaults to: 0.
redis.session.locking_enabled = 1
; How long should the lock live (in seconds)?
; Defaults to: value of max_execution_time.
redis.session.lock_expire = 60
; How long to wait between attempts to acquire lock, in microseconds?.
; Defaults to: 2000
redis.session.lock_wait_time = 10000
; Maximum number of times to retry (-1 means infinite).
; Defaults to: 10
redis.session.lock_retries = -1
- Make the redis daemon listen at a UNIX socket as well as a TCP port, uncomment these lines in the “
/etc/redis/redis.conf” configuration file:
unixsocket /var/run/redis/redis.sock
unixsocketperm 660
- Make the init script executable and start it manually (it gets added to rc.local so it will start on every boot from now on):
# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.redis
# /etc/rc.d/rc.redis start
Enable the use of redis in Nextcloud’s main configuration file “/var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/config/config.php” by adding the following block:
'memcache.locking' => '\\OC\\Memcache\\Redis',
'memcache.local' => '\\OC\\Memcache\\Redis',
'memcache.distributed' => '\\OC\\Memcache\\Redis',
'redis' =>
array (
'host' => '/var/run/redis/redis.sock',
'port' => 0,
),
Finally, allow the “apache” user to be able to read the Redis socket by adding the user to the “redis” group:
# gpasswd -a apache redis
… and restart the Apache httpd service.
PHP OPcache
OPcache is a PHP extension for Apache httpd which stores (pre-)compiled PHP script bytecode in memory. This speeds up the performance of PHP-based applications like Nextcloud, because it reduces or eliminates the need to load PHP scripts from disk and parse them every time they are called.
Slackware’s PHP has opcache enabled in “/etc/php.ini“. Relevant settings are:
opcache.enable=1
opcache.memory_consumption=128
opcache.max_accelerated_files=10000
opcache.revalidate_freq=200
These are default values for Slackware and therefore they are commented-out in the “php.ini” file but you can validate that they are enabled via the command:
# php -i |grep opcache
If you find that OPcache is disabled, you should fix that ASAP.
Check your security
Nextcloud offers a neat online tool that connects to your Nextcloud instance and performs a series of security checks, and will advise you in case you need to improve on your server security: https://scan.nextcloud.com/ .
Commandline management
The web-based management interface for the “admin” user is ‘https://darkstar.lan/nextcloud/index.php/settings/user‘ but a lot of administration tasks can also be done directly from the Slackware server’s command prompt (as root) using the “Own Cloud Console” program ‘occ‘ I already briefly touched on earlier in this article.
Some examples:
Install an application, say “richdocumentscode” which is a built-in low-performance version of CODE (Collabora Online Development Edition):
# sudo -u apache php -d memory_limit=512M /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/occ app:install richdocumentscode
App updates can be done on commandline too:
# sudo -u apache php -d memory_limit=512M /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/occ app:update --all
Remove an app:
# sudo -u apache php -d memory_limit=512M /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/occ app:remove richdocumentscode
Get the list of possible occ command options:
# sudo -u apache php -d memory_limit=512M /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/occ app:list
Integration with Keycloak IAM
The server is running nicely, and it is time to invite users. All our users will be managed by our Keycloak IAM program.
To integrate Keycloak into Nextcloud we first create a “Client ID” for Nextcloud in our Keykloak admin console and copy the relevant secret bits from that ID into Nextcloud. Nextcloud will contact Keycloak with a URL that will ebable login for the users in our “foundation” realm, i.e. the realm which we created when we setup Keycloak.
Keyloak:
- Login to the Keycloak Admin Console, https://sso.darkstar.lan/auth/admin/ .
- Under ‘Clients‘, create a new client:
‘Client ID‘ = “nextcloud”
‘Root URL‘ = “darkstar.lan/nextcloud“
- Save.
- In the ‘Settings‘ tab, change:
‘Access Type‘ = “confidential” (default is “public”)
- Save.
- In the ‘Credentials‘ tab, copy the value of the ‘Secret‘, which we will use later in Nextcloud: “
61a3dfa1-656d-45eb-943a-f3579a062ccb” (your own value will of course be different).
Nextcloud:
- Login to Nextcloud as the admin user: https://darkstar.lan/nextcloud
- In ‘Profile > Apps‘, install the ‘Social Login‘ app.
- Configure Nextcloud’s social login to use Keycloak as the identity provider
- Make sure ‘Disable auto create new users‘ is UN-checked because every user logging in via Keycloak for the first time must automatically be created as a new user.
- DO check ‘Prevent creating an account if the email address exists in another account‘ to ensure that everyone will have only one account
- Add a new ‘Custom OpenID Connect‘ by clicking on the ‘
+‘:
‘Title’ = “keycloak”
‘Authorize url’ = “https://sso.darkstar.lan/auth/realms/foundation/protocol/openid-connect/auth”
‘Token url’ = “https://sso.darkstar.lan/auth/realms/foundation/protocol/openid-connect/token”
‘Client id’ = “nextcloud”
‘Client Secret’ = “61a3dfa1-656d-45eb-943a-f3579a062ccb” (this is the value you obtained earlier in the Keycloak Client definition)
‘Scope’ = “openid”
‘Default group’ = “none”
- ‘Groups claim’ = “nextcloud” (optional setting, make sure you create a group “nextcloud” in Keycloak’s “foundation” realm and have added your future Nextcloud users as members of this group).
- Also optional, ‘Add group mapping‘ can automatically arrange that the Keycloak group “nextcloud” is mapped to Nextcloud group, e.g. called “My social circle” with which you can limit access in Nextcloud to only those apps that you approved.
- Save.
Your Nextcloud login page will now additionally offer a ‘Login with Keycloak Authentication” option. Clicking this will redirect you to a Keycloak authentication page. Screenshots of how this looks exactly can be found further down in the section “Nextcloud clients“.
After successful login and authorization with an existing Keycloak user account you will be returned to Nextcloud and logged in. If this was the user’s first login to Nextcloud using Keycloak credentials, Nextcloud will create an internal user account which is linked to the Keycloak credentials.
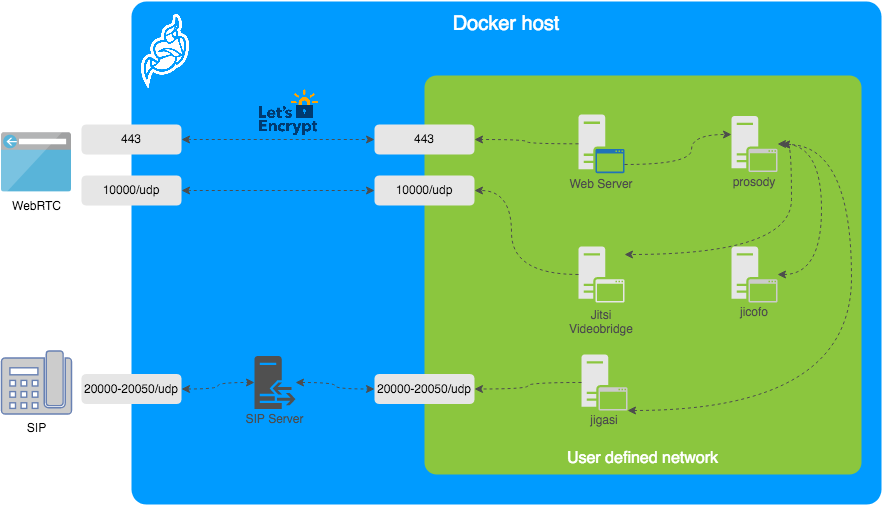
Integrating Jitsi Meet
The integration of an embedded Jitsi Meet window into Nextcloud requires some configuration in Apache httpd (for the embedding) and in Nextcloud itself (securing the intercommunication via a JSON Web Token).
Apache:
Add the following to your httpd global configuration, for instance to ‘/etc/httpd/httpd.conf‘ (the parts in green need to be replaced by your real-life hostnames of course):
# Mitigate the risk of "click-jacking" (other sites embedding your pages
# and adding other, possibly malicious, content)
# See https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/HTTP/X-Frame-Options
Header always append X-Frame-Options SAMEORIGIN
# And allow embedding of Jitsi Meet in Nextcloud (add any URL for which you would also allow embedding):
RequestHeader set X-HTTPS 1
Header always set Content-Security-Policy "frame-ancestors 'self';"
Header always set Content-Security-Policy "frame-ancestors https://darkstar.lan https://sso.darkstar.lan https://meet.darkstar.lan ;"
Followed by a restart of Apache httpd.
Nextcloud:
- Install the “Jitsi Integration” app as the admin user via ‘Profile > Apps‘
- Go to ‘Profile >Settings > Jitsi’
- ‘Server URL’: enter “https://meet.darkstar.lan“
- ‘JWT Secret’: enter “NmjPGpn+NjTe7oQUV9YqfaXiBULcsxYj” (this is the JWT token which you entered as the value for ‘JWT_APP_SECRET‘ variable in the ‘
.env‘ file of our ‘docker-jitsi-meet‘ instance, see the previous Episode on Video Conferencing for details)
- ‘JWT App Id‘: enter “jitsi” (which is the value of the ‘JWT_APP_ID‘ variable in that same ‘
.env‘ file)
- Save
That’s it!
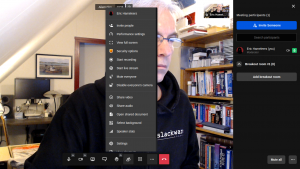
Users will now find a ‘Conferences‘ icon in the application bar at the top of their Nextcloud home. Clicking it will open an embedded Jitsi video conferencing window.
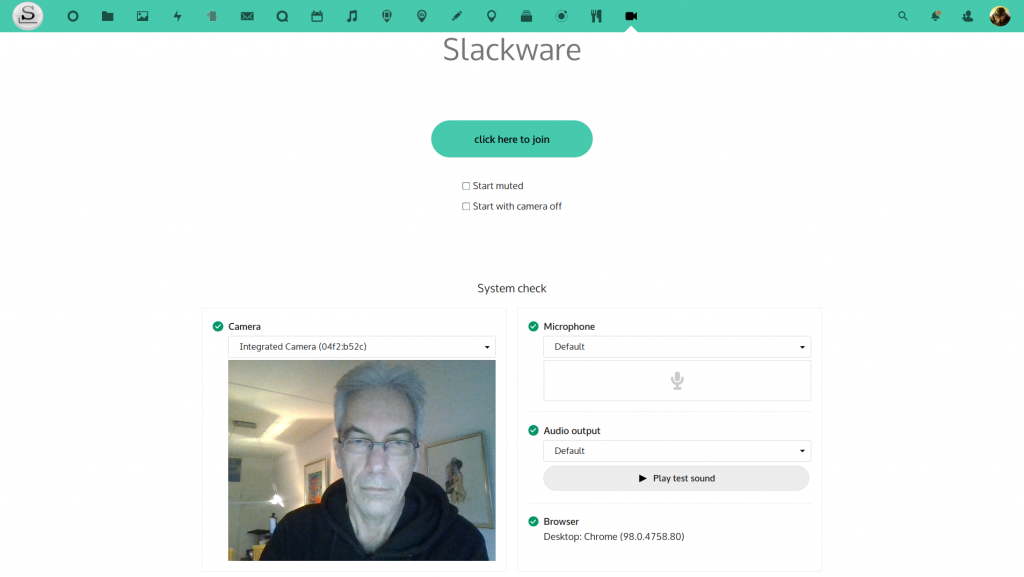
One obvious advantage to using this NextCloud embedded Jitsi Meet is that the resulting Meet URLs are impossible to guess, they will not mention the meeting room name but instead use a UUID like ‘https://meet.darkstar.lan/06135d8e-5365-4a6f-b31b-a654d92e8985‘.
If you compare this to the regular Jitsi Meet at ‘https://meet.darkstar.lan/‘, your meeting room with the name ‘roomname‘ would be accessible as ‘https://meet.darkstar.lan/roomname‘ which is a lot easier to guess… un-desirable if you want to hold private meetings.
Adding new apps
I encourage you to check out the Nextcloud App Store. There’s a wealth of cool, useful and fun applications to be found there.
Some of the apps that I installed are: GPXPod (visualize your GPX routes); Carnet (powerful note-taking app); Music (listen to your local collection or tune into online streams); PhoneTrack (keep track of your phone, needs the Android app to be installed too); Element (messenger app with bridges to Matrix and Libera.Chat for instance); Cookbook (maintain your own recipe database and easily import new recipes from external websites using only the URL to the recipe), etc…
Adding client push daemon
Extremely useful is Push update support for the desktop app. The 21 release of Nextcloud introduced a ‘high performance backend‘ for filetransfers. This increases the speed of filetransfers substantially, but it needs a couple of things to make it work.
- The worker app is called “Client Push” and needs to be installed on your server from the Nextcloud App Store. Once the app is installed, the push binary still needs to be setup. The README on github contains detailed setup instructions. For the Slackware way, read on.
- You need to have the redis package installed and the redis server needs to be started and running. We already took care of this in the section ‘Performance tuning‘.
- Slackware, Apache and Nextcloud need to be configured for redis and the notify_push daemon.
Slackware:
The notify_push binary gets installed as ‘/opt/nextcloud/localapps/notify_push/bin/x86_64/notify_push‘. Hint: this is 64-bit only. This binary needs to run always, so the easiest way is to add a Slackware init script and call that in ‘/etc/rc.d/rc.local‘.
The init script can be downloaded from my repository, but it’s listed here in full as well. I highlighted the texts in green that are relevant. Save it as ‘/etc/rc.d/rc.ncpush‘ and make it executable:
#!/bin/bash
# Description: Push daemon for NextCloud clients.
# Needs: redis php-fpm mariadb
# Written by: Eric Hameleers <alien@slackware.com> 2021
daemon=/usr/bin/daemon
description="Push daemon for Nextcloud clients"
pidfile=${pidfile:-/var/run/nextcloud/notify_push.pid}
ncconfig=${ncconfig:-/var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/config/config.php}
command=${command:-/opt/nextcloud/localapps/notify_push/bin/x86_64/notify_push}
command_user=${command_user:-apache}
command_args="--bind 127.0.0.1 --port 7867 $ncconfig"
[ ! -x $command ] && exit 99
[ ! -f $ncconfig ] && exit 99
RETVAL=0
start() {
if [ -e "$pidfile" ]; then
echo "$description already started!"
else
echo -n "Starting $description: "
mkdir -p $(dirname $pidfile)
chown $command_user $(dirname $pidfile)
chmod 0770 $(dirname $pidfile)
$daemon -S -u $command_user -F $pidfile -- $command $command_args
RETVAL=$?
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && touch /var/lock/subsys/$(basename $command)
echo "- done."
fi
}
stop(){
echo -n "Stopping $description: "
kill -TERM $(cat $pidfile)
RETVAL=$?
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && rm -f /var/lock/subsys/$(basename $command)
echo "- done."
}
restart(){
stop
start
}
condrestart(){
[ -e /var/lock/subsys/$(basename $command) ] && restart
}
status() {
pids=$(cat $pidfile 2>/dev/null)
if test "$pids" ; then
echo "$description is running."
ps up $pids
else
echo "$description is stopped."
fi
}
# See how we were called.
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
status)
status
;;
restart)
restart
;;
condrestart)
condrestart
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart}"
RETVAL=1
esac
exit $RETVAL
# ---
The script is then called on boot by adding the following to your server’s ‘/etc/rc.d/rc.local‘:
if [ -x /etc/rc.d/rc.ncpush ]; then
# Start Nextcloud Client Push Daemon
echo "Starting Nextcloud Client Push Daemon: /etc/rc.d/rc.ncpush start"
/etc/rc.d/rc.ncpush start
fi
Apache:
Setup the bits of Apache configuration for your webserver. The following block of configuration needs to be added:
ProxyPreserveHost On
ProxyTimeout 900
SSLProxyEngine on
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Proto "https"
# Setup a reverse proxy for the client push server
# https://github.com/nextcloud/notify_push/blob/main/README.md :
<Location /push/ws>
ProxyPass ws://127.0.0.1:7867/ws
</Location>
<Location /push/>
ProxyPass http://127.0.0.1:7867/
ProxyPassReverse http://127.0.0.1:7867/
</Location>
# Do not forget WebSocket proxy:
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Connection} Upgrade [NC]
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Upgrade} websocket [NC]
You know where to add the above.
Nextcloud:
Add these lines to “./config/config.php“. Relevant pieces are highlighted in green, you should of course change that into your own Internet IP address:
‘trusted_proxies’ => [‘10.10.10.10‘],
‘forwarded_for_headers’ => [‘HTTP_X_FORWARDED’, ‘HTTP_FORWARDED_FOR’, ‘HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR’],
Piecing it all together:
Preparations are complete after you have restarted Apache httpd and started the ‘rc.ncpush‘ script. Redis should also be running.
Now we can finally enable the app we installed in Nextcloud:
# sudo -u apache php -d memory_limit=512M /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/occ app:enable notify_push
Setup the connection between the app and the daemon:
# sudo -u apache php -d memory_limit=512M /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/occ notify_push:setup https://darkstar.lan/push/
> redis is configured
> push server is receiving redis messages
> push server can load mount info from database
> push server can connect to the Nextcloud server
> push server is a trusted proxy
> push server is running the same version as the app
configuration saved
Upgrading to newer release
Here is an example of the steps to take when you upgrade from one major release to the next (for instance you want to upgrade from 23 to 24).
First, download and extract the release tarball, and set the file ownership to the ‘apache‘ user:
# cd ~
# wget https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/nextcloud-24.0.0.tar.bz2
# tar xf nextcloud-24.0.0.tar.bz2
# chown -R apache:wheel /root/nextcloud
Disable the server-maintenance cronjob of the “apache” user before continuing, for instance by adding ‘#” in front of the cron commandline!
# crontab -u apache -e
# crontab -u apache -l
# Run maintenance for NextCloud every 5 minutes:
####*/5 * * * * /usr/bin/php -f /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/cron.php
Stop the Apache httpd:
# /etc/rc.d/rc.httpd stop
Rename the old “/var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/” installation directory and move the new ‘nextcloud‘ directory in its place:
# mv -i /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud /root/nextcloud.orig
# mv -i /root/nextcloud /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud
Copy your Nextcloud configuration into the new directory (this should only overwrite the ‘config.sample.php‘ file):
# cp -ia /root/nextcloud.orig/config/* /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/config/
Start the Apache httpd again:
# /etc/rc.d/rc.httpd start
Start the commandline updater. This MUST be done from within the Nextcloud installation directory:
# cd /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/
# sudo -u apache php -d memory_limit=512M occ upgrade
Now, re-enable the cronjob for user “apache“.
Then re-create the now again missing database indices:
# sudo -u apache php /var/www/htdocs/nextcloud/occ db:add-missing-indices
Stable versus beta channels
Nextcloud offers “Stable” and “Beta” channels of its software. From time to time, new functionality becomes available in the Beta channel that you really want to use.
As the admin user, you can configure your preferred release channel in “Settings > Administration > Overview > Version > Update Channel” if you have installed Nextcloud from a release tarball like we did.
NOTE that you can only upgrade to a newer version. Skipping major versions when upgrading and downgrading to older versions is not supported by Nextcloud.
For instance, if you went via ‘Beta‘ to 24.0.0rc4 and ‘Stable‘ is still on 23.0.5, you have to wait with further upgrades until 24.0.0 or later becomes available in the ‘Stable‘ channel.
Nextcloud makes new versions incrementally available to user installations in the Stable channel which means it can take a while before your server alerts you that a new release is available.
Nextcloud clients
Nextcloud mobile and desktop clients are available from https://nextcloud.com/clients/ .
Client applications can keep your files synchronized between Nextcloud server and your desktop or phone; can manage your passwords that you store securely on the server; can manage your calendar, setup chat and video connections to other users of your server; and more.
The desktop file-sync client (nextcloud-client) is available in my own repository as a package and on SlackBuilds.org as a build script (but the SBo version is actually still the old OwnCloud mirall client). Its GUI is Qt5-based. This is a free alternative for Dropbox and the likes!
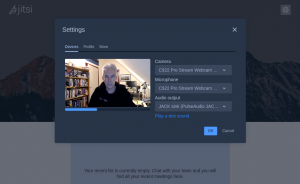
When you start the nextcloud-client desktop application for the first time, you will go through an initial setup. The client needs to get configured to connect to your Nextcloud server:
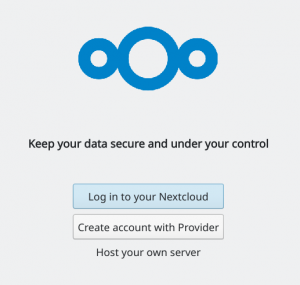
After clicking “Log in to your Nextcloud” you can enter the URL at which your server is available:
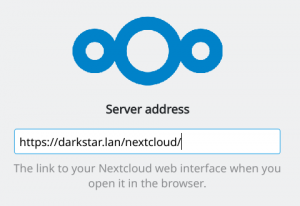
The client will open your default browser (in case of my KDE Plasma5, this was Konqueror) and ask you to switch to that browser window to logon to your Nextcloud:
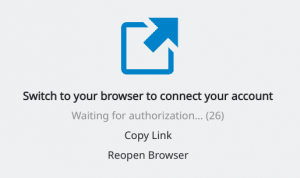
You can click “Copy Link” so that you can use another browser if you are not happy with the default browser choice. The next steps take place inside that browser window:
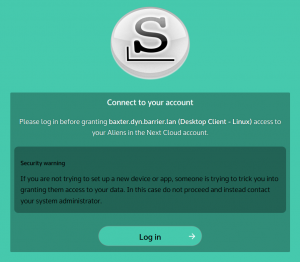
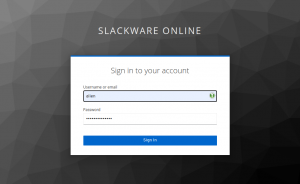
You need to login with your Nextcloud user account. In this dialog we click on “Log in with Keycloak Authentication” instead of entering an account/password into the top entry fields – remember, only the admin user has an account with local credentials:
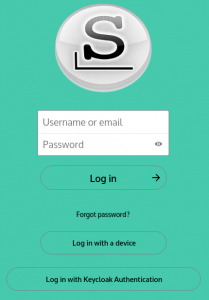
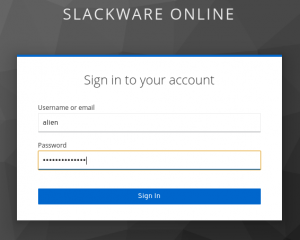
You will probably recognize the familiar Keycloak Single Sign On dialogs from the previous Episode (Video Conferencing):
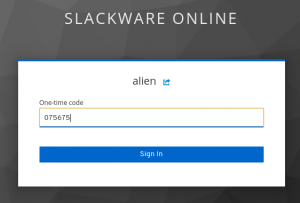
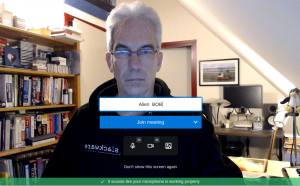
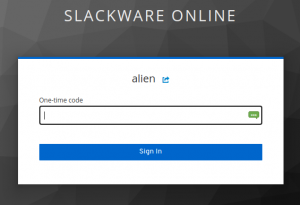
This account has 2-Factor Authentication (2FA) enabled:
After succesful login, the Nextcloud server wants to get your explicit permission to grant access for the desktop client to your server data:
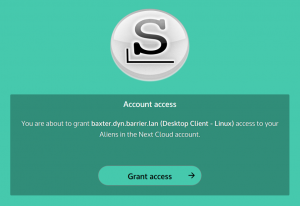
After you click “Grant access” the client will finally be able to connect to your data and start syncing:

You get a choice of the local desktop directory to synchronize with your server data – by default this is ‘~/Nextcloud/‘:
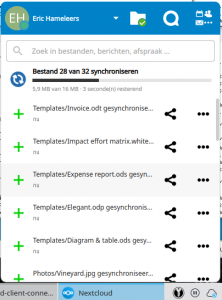
The client docks into the system tray from where you can access your files and manage the sync. The desktop client integrates nicely with KDE’s Dolphin and Konqueror, and shows the sync status of the ‘~/Nextcloud/‘ directory (and the files in it) with a badge – similar to what Dropbox does.
All files inside ‘~/Nextcloud/‘ will have a right-mouseclick context menu offering some filesharing options and the possibility to open the serverlocation of the file in your webbrowser.
Fixes
To end this Episode, I will collect the fixes that were necessary to make Nextcloud do what I wanted it to do.
Enable geolocation in the NextCloud phonetrack app by applying this patch:
# diff -u lib/public/AppFramework/Http/FeaturePolicy.php{.orig,}
--- lib/public/AppFramework/Http/FeaturePolicy.php.orig 2021-10-02 12:57:56.1506
83402 +0200
+++ lib/public/AppFramework/Http/FeaturePolicy.php 2021-10-11 15:38:01.2146
23284 +0200
@@ -49,7 +49,9 @@
];
/** @var string[] of allowed domains that can use the geolocation of the
device */
- protected $geolocationDomains = [];
+ protected $geolocationDomains = [
+ '\'self\'',
+ ];
/** @var string[] of allowed domains that can use the microphone */
protected $microphoneDomains = [];
Thanks
Thanks for reading all the way to the end of this Episode. I hope you learnt from it and are eager to try this Nextcloud platform on your own private Slackware Cloud Server!
As always, leave constructive and helpful feedback in the comments section below.
Cheers, Eric
 A spin-off from our previous Episode in this series is this fifth article about using Slackware as your private/personal ‘cloud server’.
A spin-off from our previous Episode in this series is this fifth article about using Slackware as your private/personal ‘cloud server’.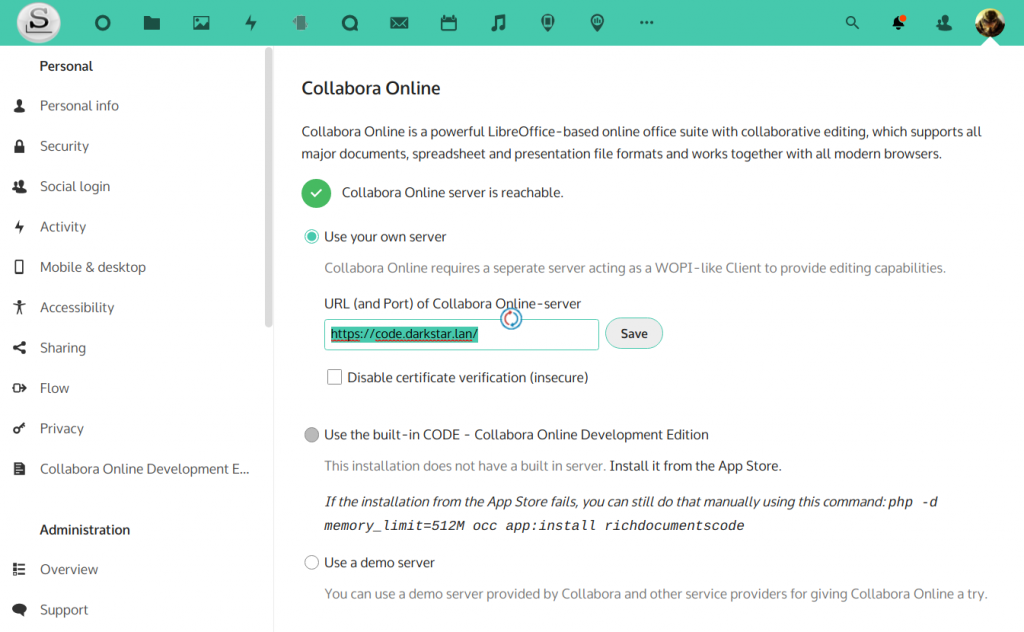 The configuration boils down to:
The configuration boils down to:
 LibreOffice Community Edition
LibreOffice Community Edition 















 I honestly kept my breath and have had some difficulty believing that this would eventually really happen, but yet here it is. Slackware 15.0 stable! Released yesterday and available on mirrors across the globe today.
I honestly kept my breath and have had some difficulty believing that this would eventually really happen, but yet here it is. Slackware 15.0 stable! Released yesterday and available on mirrors across the globe today.
Recent comments